Spatial Information Science (SIS)
SIS: Collecting, processing, analysing and visualising data to produce and validate spatial information while being acutely aware of the provenance of the data (its metadata) and data uncertainty.
Objective
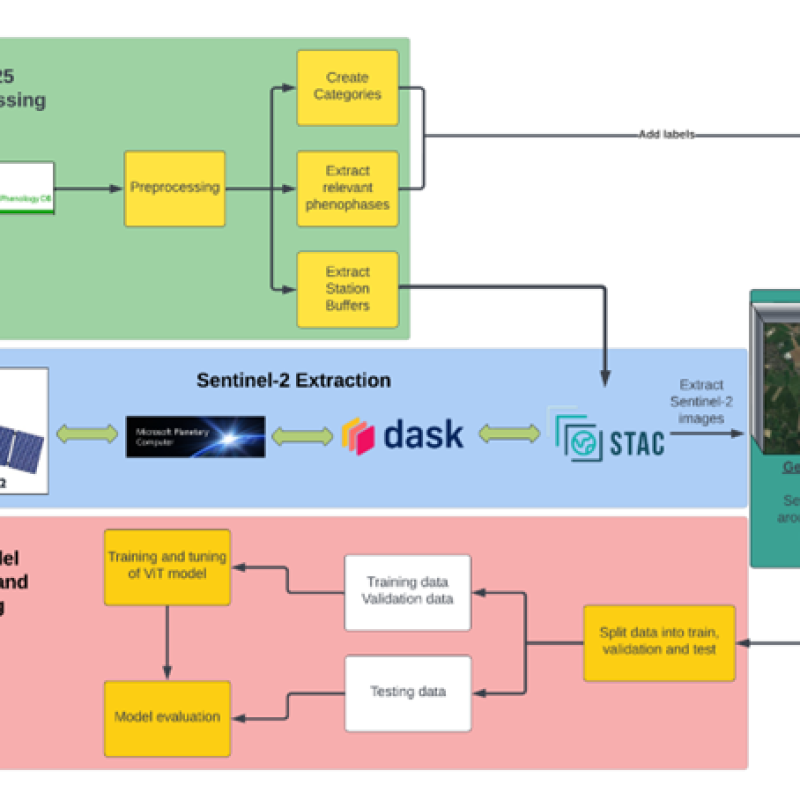
To develop a deep learning model to estimate the timing of phenological events over large area
The topic can take several directions depending on the interest of the student.
To develop a model to estimate the timing of phenological events over large areas from time series of earth observation data using vision transformers, a fierce alternative to tra
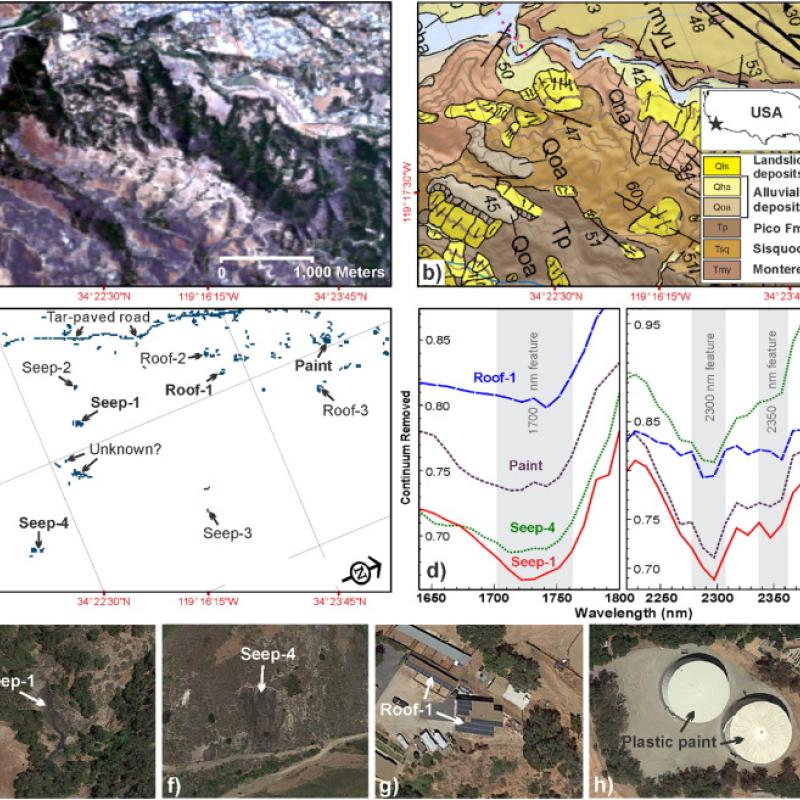
Global production, transportation, and consumption of oil can cause inevitable spills into the environment (typically from pipelines, oil wells, and storage facilities) cont
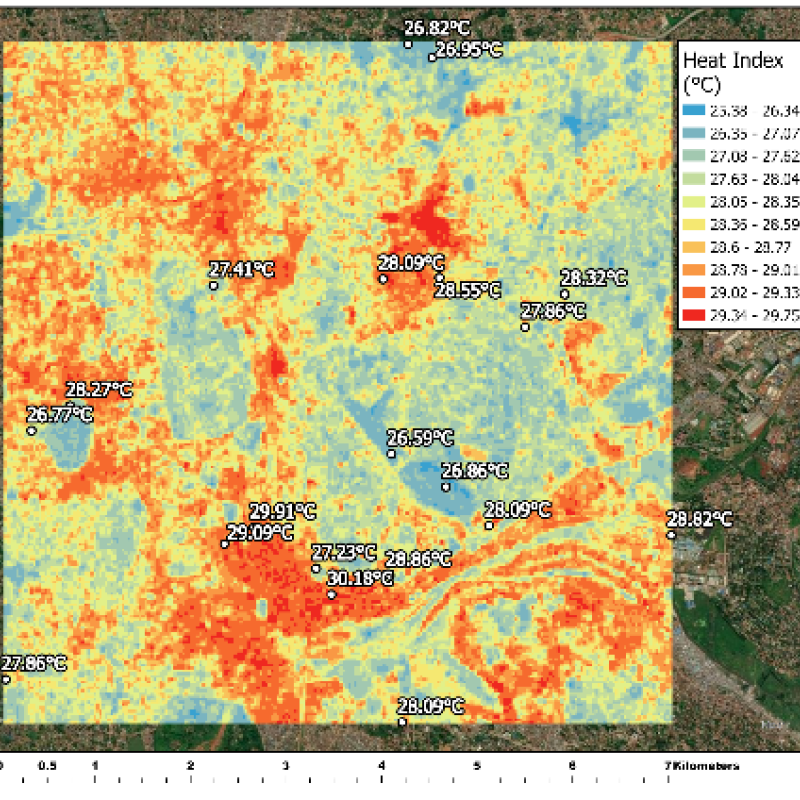
The climate in cities and metropolitan areas (i.e., urban climate) is often different from the climate in the surrounding rural areas due to the presence of buildings, pavement, a
These days simple tools exist that allow everyone to make maps, and subsequently use social media to disseminate the maps, with can reach millions.
ITC has been supporting UN-Habitat, the United Nations organization for urban development, since 2011 with the development and implementation of a regional urban planning approach
The Antarctic ice sheet covers almost the whole area of the Antarctic continent.
Rainfall data series from climate models (i.e.
This study aims to assess the applicability of satellite rainfall estimates (SRE) in crop growth modelling by means of the Aquacrop model.