Spatial Information Science (SIS)
SIS: Collecting, processing, analysing and visualising data to produce and validate spatial information while being acutely aware of the provenance of the data (its metadata) and data uncertainty.
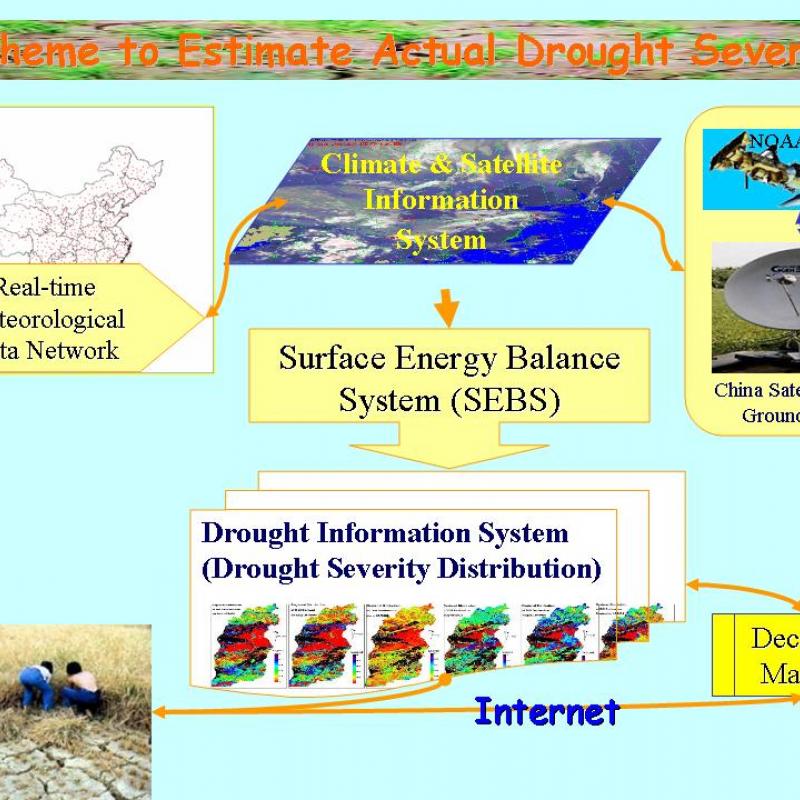
Drought has wreaked havoc to human societies throughout history. Drought is usually caused by a multitude of factors starting from the deficit of precipitation when compared to climatic mean.
Thermal remote sensing is a type of passive remote sensing since that detects naturally emitted radiation. Most thermal remote sensing for vegetation conducted in the 8-14 μm wavelengths.
A key task for conservation science is to collect accurate and precise data on animal distribution.
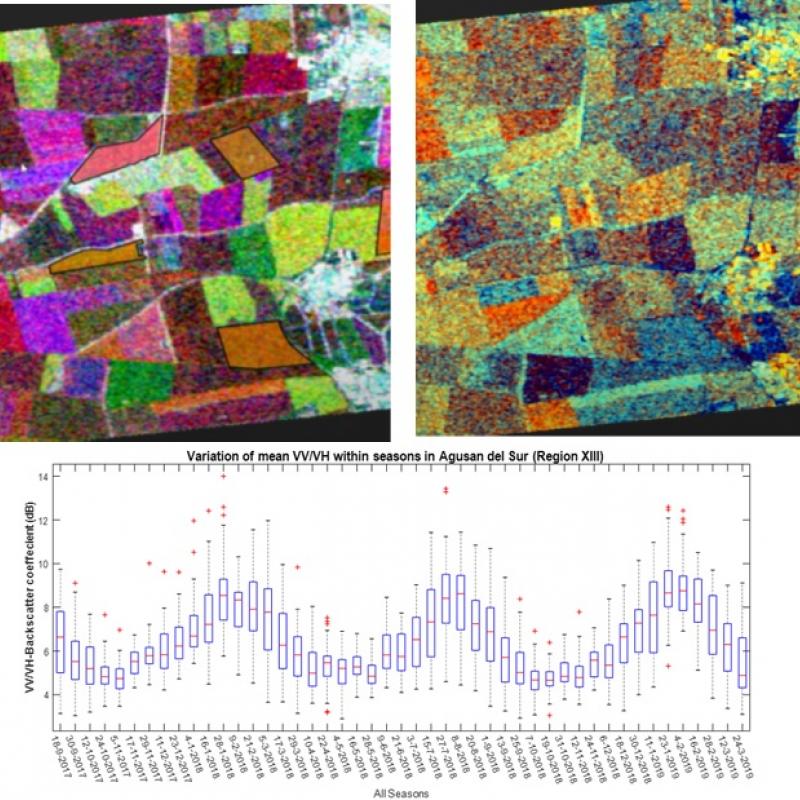
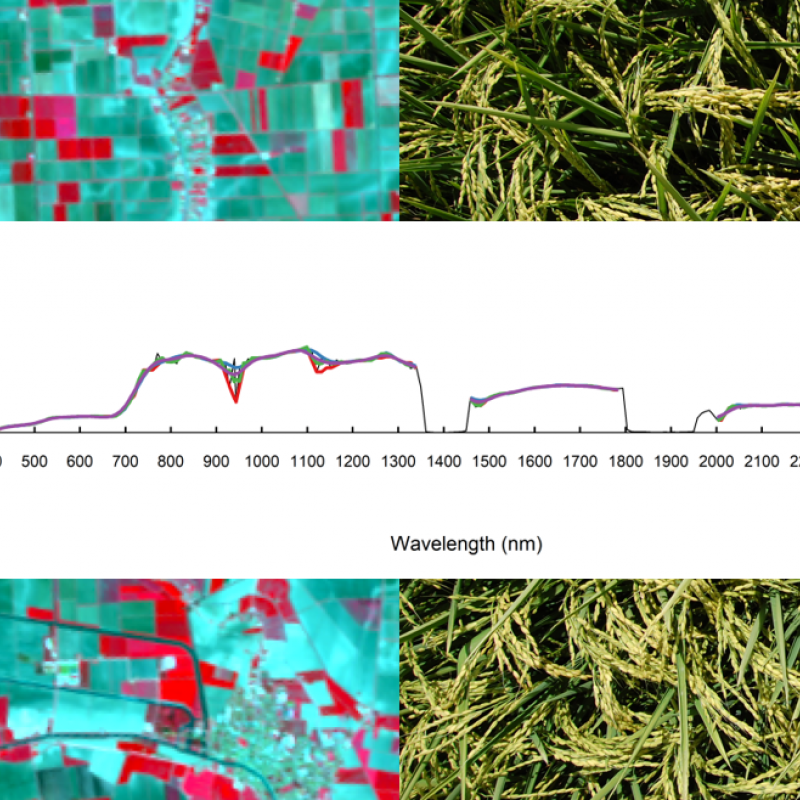
To inform policymakers about the agricultural landscapes and food production, accurate and timely monitoring of crop type is required.
Farmers, agronomists, private enterprise and policy-makers need to know field conditions with sufficient early-warning.
Amazingly, the Dutch nature conservation monitoring system makes very little use of remote sensing.
LAI is one of the most critical vegetation biophysical variables as well as remote sensing- enabled essential biodiversity variables due to the controlling role of green leaves in biological and ph
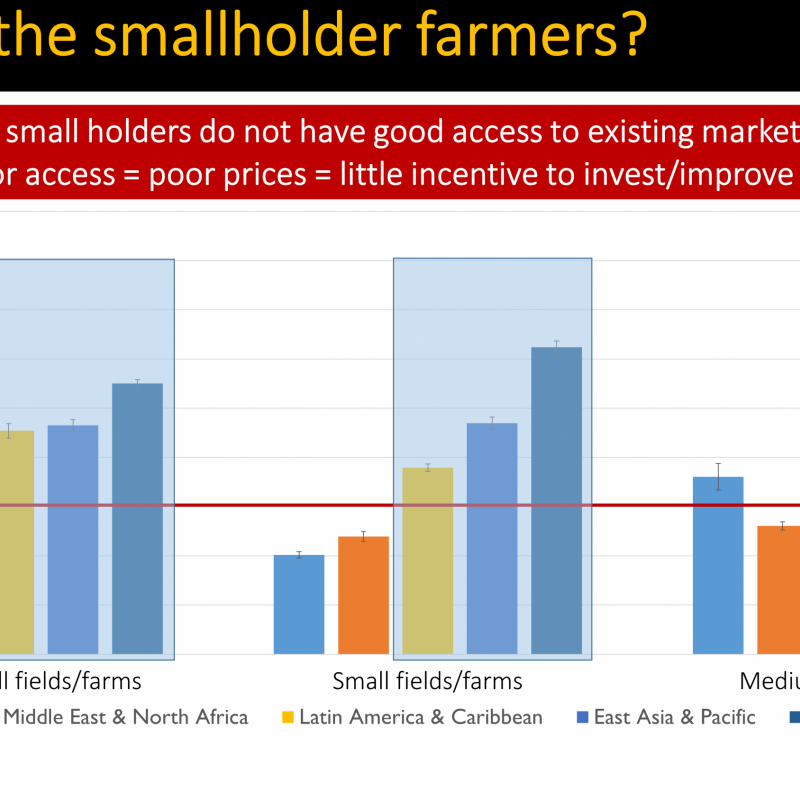
Good access to resources and opportunities is essential for sustainable development. Improving
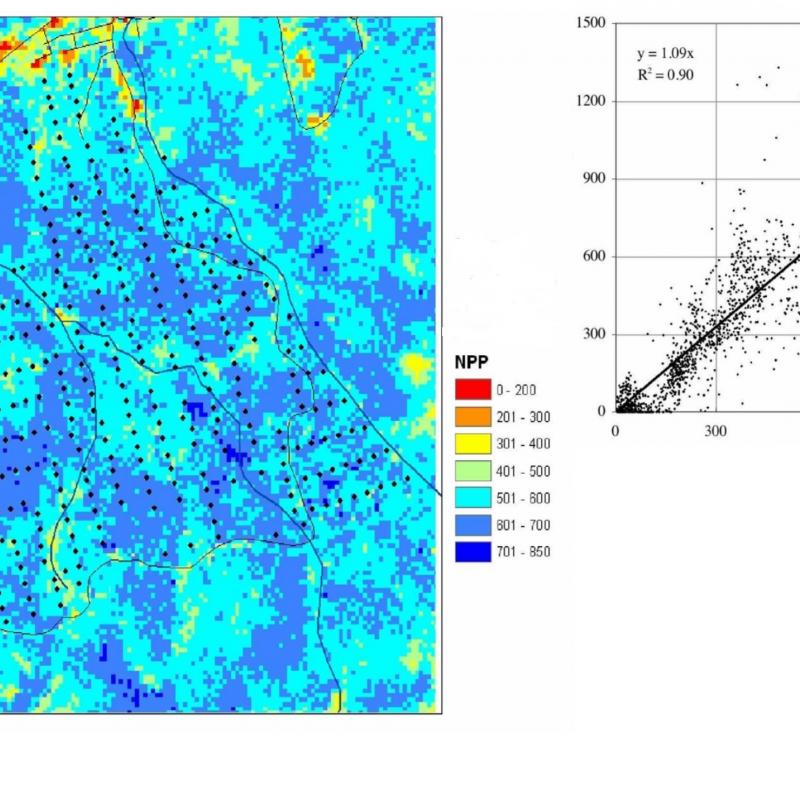
Primary production is the growth or accumulated rate of biomass in plants.
The goal of sustainable transport is to promote better and healthier ways for individuals and communities to meet their travel needs while reducing the negative social, environmental and economic i