Spatial Information Science (SIS)
SIS: Collecting, processing, analysing and visualising data to produce and validate spatial information while being acutely aware of the provenance of the data (its metadata) and data uncertainty.
The goal of this study, as part of the larger BIOSPACE project, is to map and model leaf and canopy nitrogen content and their spatial va
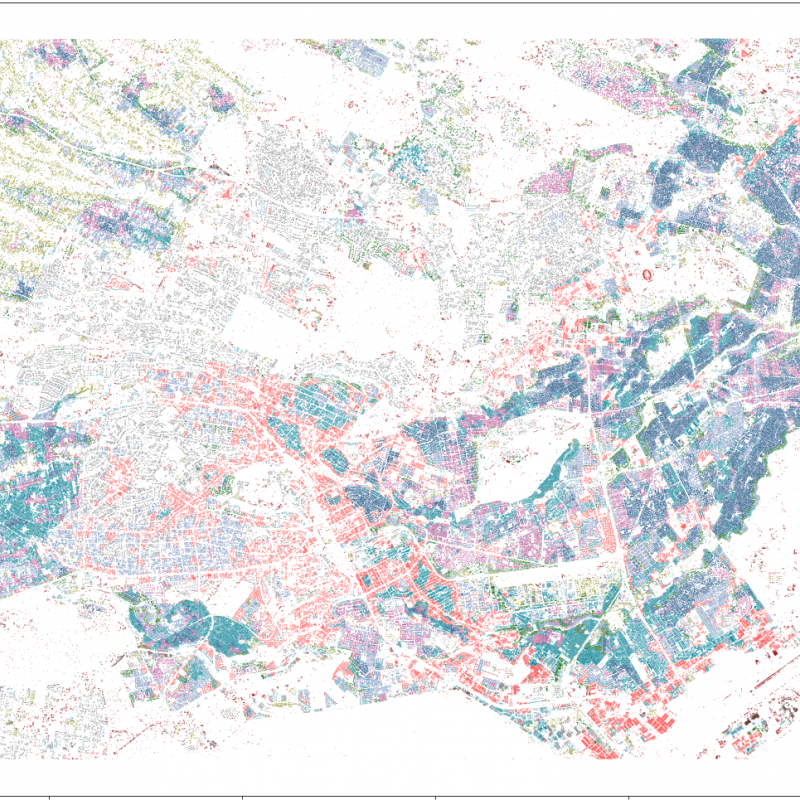
Student will use earth observation based data and techniques to understand urban socioeconomic patterns, and attempt to interpret these patterns by using physical metrics of urban morphology obtain
Concept: Nipah, a deadly viral disease is confined only to a small pocket of Kerala.
Concept: Kerala is highly prone to variety of natural hazards, such as cyclones, flood, landslides, drought and heatwaves.
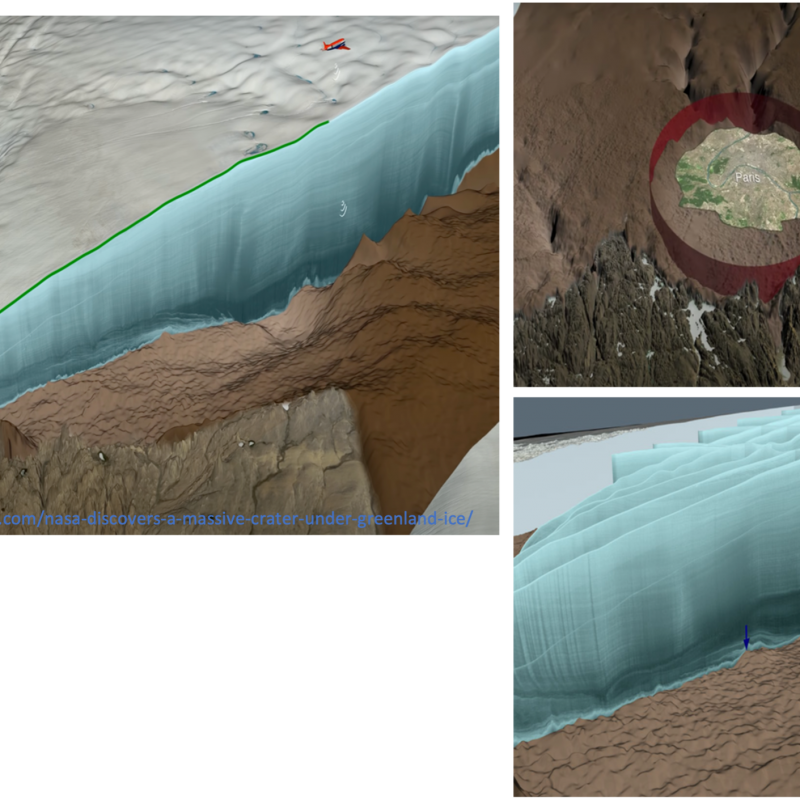
Downward-looking satellite sensors are used to display our three-dimensional (3D) world with 2D remote sensing imagery.
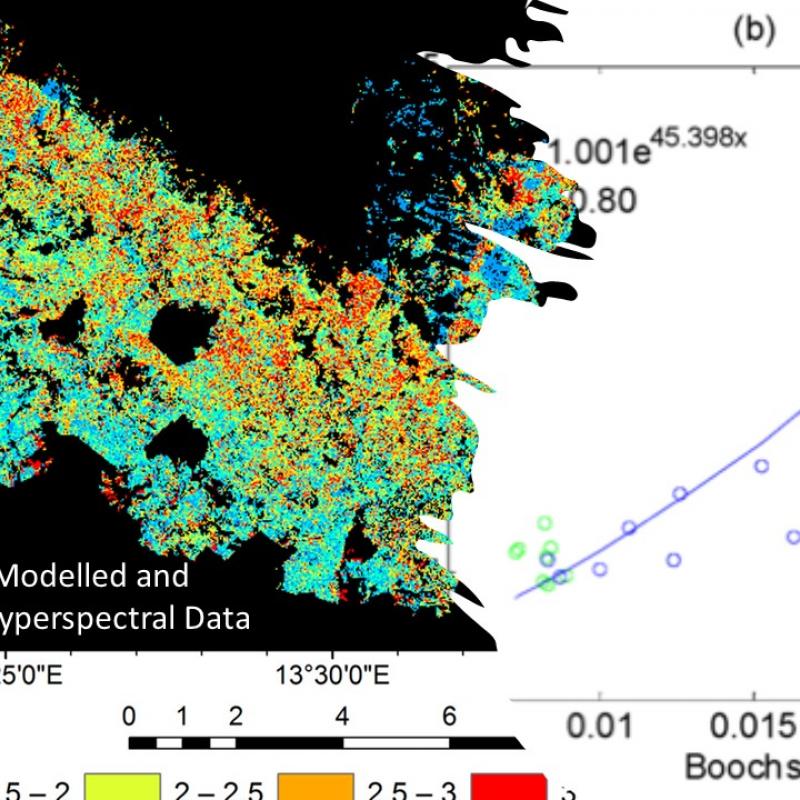
Aboveground forest biomass has fundamental role in carbon cycling, climate processes, and global warming.
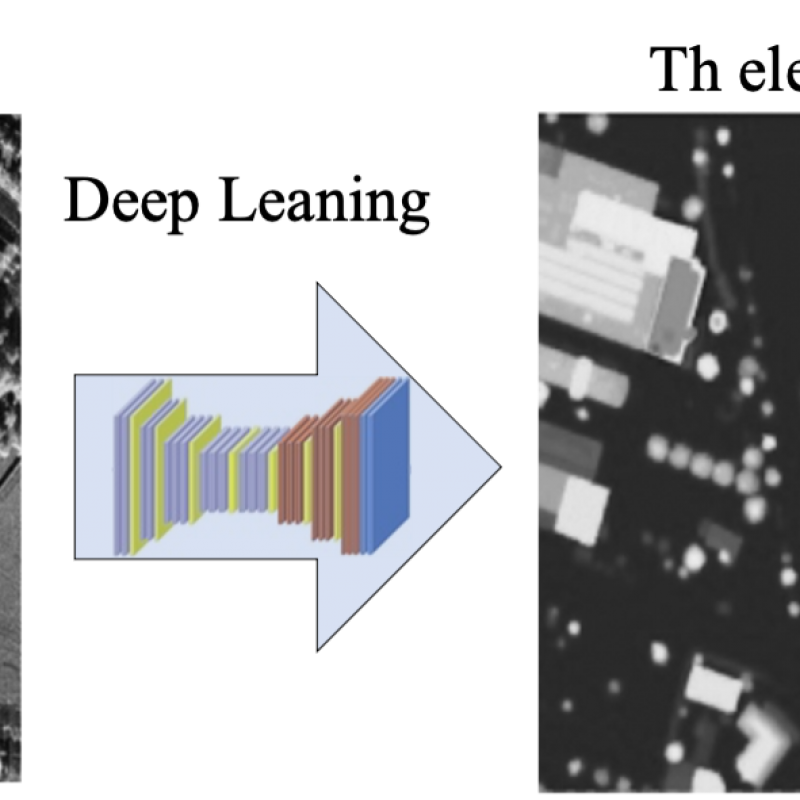
The student will initially revise the existing literature on image matching algorithms using CNN as backbone.
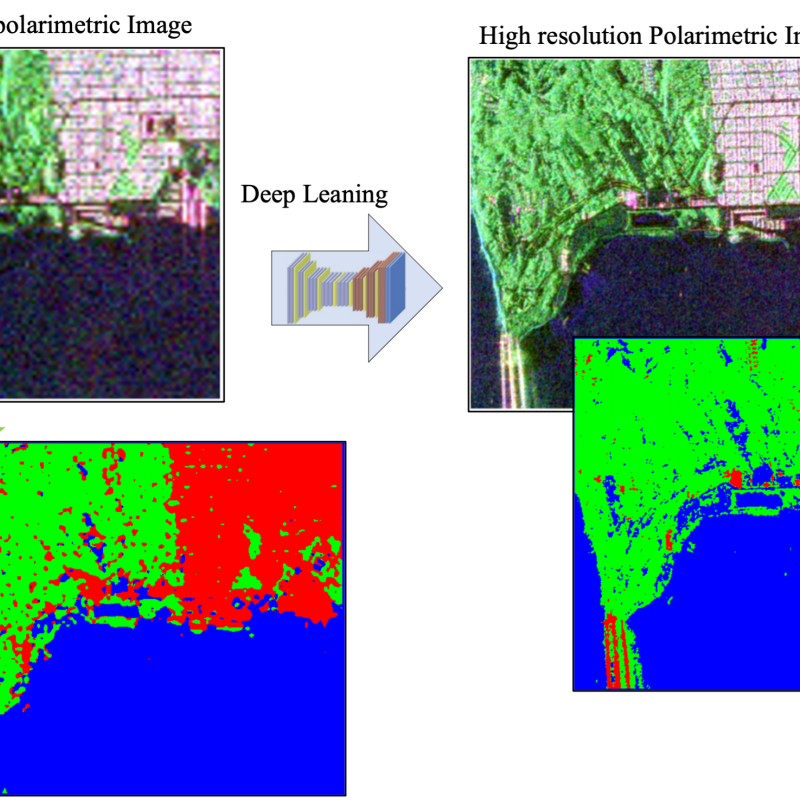
Sentinel-1, with a constellation of radar satellites, operates day and night, providing freely accessible, consistent, and time series SAR images of every part of the Earth.
Information on the spatial distribution of crops is of great importance for the sustainable management and development of agricultural practices and thus for national and global economic developmen