Integration of remote sensing and social media data for generating training samples and mapping the impervious surfaces

Impervious surfaces are the Earth’s surfaces covered with mainly anthropogenic and artificial structures, such as built-up areas, roads and streets, and parking lots. Analyzing the spatial distribution of the impervious surfaces plays a key role in ecological and urbanization studies.
In recent years, remote sensing technologies have shown to be effective tools for the estimation of the Earth’s impervious surfaces. Many techniques have been proposed to exploit valuable information extracted from the remote sensing data. In particular, the use of machine learning classification techniques has been suggested in several works to improve the speed and accuracy of the estimation. Despite the advantage of classification techniques, it is still challenging to define meaningful classes and obtain sufficient and timely training data. Thus, there is still a strong need to develop innovative solutions.
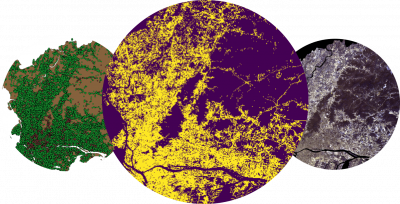
Recently, social media has received growing attention in the remote sensing community [1]. Particularly, the relationship between land use and the geo-referenced social media feeds (e.g., from Twitter) has been explored and applied in several studies [2]. This study's primary objective is to exploit such a relationship and implement an automatic approach for generating training samples from geo-referenced social media data and apply it in a classification system for impervious surface estimation from satellite (e.g., Sentinel-2) images. The focus of this study is on the imperious surface mapping in developing countries. A massive dataset of geotagged tweets is available in GIP that can be used in this study.
Developing a classification system based on the integration of remote sensing and social media data for estimating the impervious surfaces
- [1] Yu, Y., Li, J., Zhu, C., & Plaza, A. (2018). Urban impervious surface estimation from remote sensing and social data. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 84(12), 771-780.
- [2] Miao, Z., Xiao, Y., Shi, W., He, Y., Gamba, P., Li, Z., & Wu, H. (2019). Integration of satellite images and open data for impervious surface classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 12(4), 1120-1133.
